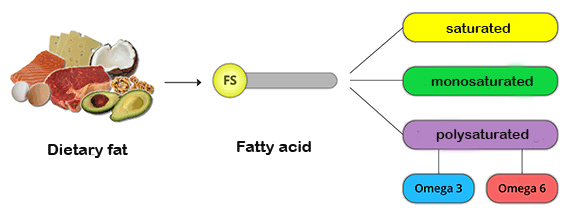
The individual fatty acids are named according to different points of view. On the one hand, the number of carbon atoms (18, 20, ...) and the number and position of the double bond within the fatty acid are designated.
The C atoms are numbered from the fat-soluble (omega) end of the fatty acid and thus given the designation omega-3 or omega-6 or omega-9, i.e. the first double bond is located at C 3, 6 or 9 atoms.
For the double bond itself it is still important whether the hydrogen atoms are in cis or trans configuration.
The polyunsaturated fatty acids are essential, i.e. essential for life, and must be supplied with food.
However, it is very important that the various polyunsaturated fatty acids are in a certain balance.
If this is disturbed, the cybernetic system consisting of inflammation promotion and inflammation prevention begins to falter. In the end, all this happens at the level of the interleukins.